A CT (computerised tomography) scan is a painless, non-invasive imaging test. It uses low-dose X-rays and a computer to produce detailed images of many structures inside the body, including the internal organs, blood vessels and bones. CT scans are used to help detect diseases and injuries.
What is a CT scan for?
You may be recommended a CT scan to diagnose any disease of the lungs, heart, brain, and organs in the abdomen and pelvis. It is also used following injuries to the bones and spine.
A CT scan can also be used to detect problems with the blood vessels, as well as to detect tumours (both malignant and benign) in different parts of the body.
If you have symptoms which suggest one of the above diseases or conditions, your doctor may recommend that you have a CT scan to determine the cause of your symptoms.
Similarly, if you have been previously diagnosed with a disease or condition, a CT scan can help you and your doctor to monitor the condition and prescribe any further medication or treatment required.
Types of CT scans
We offer several types of CT scans, depending on which part of your body requires examination, whether you have been previously diagnosed with a disease or condition, and what symptoms you have had prior to the scan.
CT coronary angiogram
A cardiac CT scan takes pictures of your heart and builds a complete three-dimensional picture of the organ. This enables the clinician to look for any heart problems including any plaques using a dye (also called a contrast), which is injected via a vein in your arm. The images also reveal any narrowing or blockage of the arteries around your heart.
CT coronary calcification
A CT coronary calcification score scan allows us to quantify the presence of calcium (calcified plaques) in the coronary arteries and is considered a test that identifies patients at risk of having heart disease.
Lung CT
A lung or chest CT scan allows us to look at different levels of the chest and lungs and provides a more detailed picture than standard chest X-rays. This test can help find the causes of shortness of breath and chest pain, and to identify other diseases such as lung tumours, emphysema or tuberculosis.
General CT
Our team can also provide most general CT scans including reporting for head and neck, extremities, and body scans including vascular imaging.
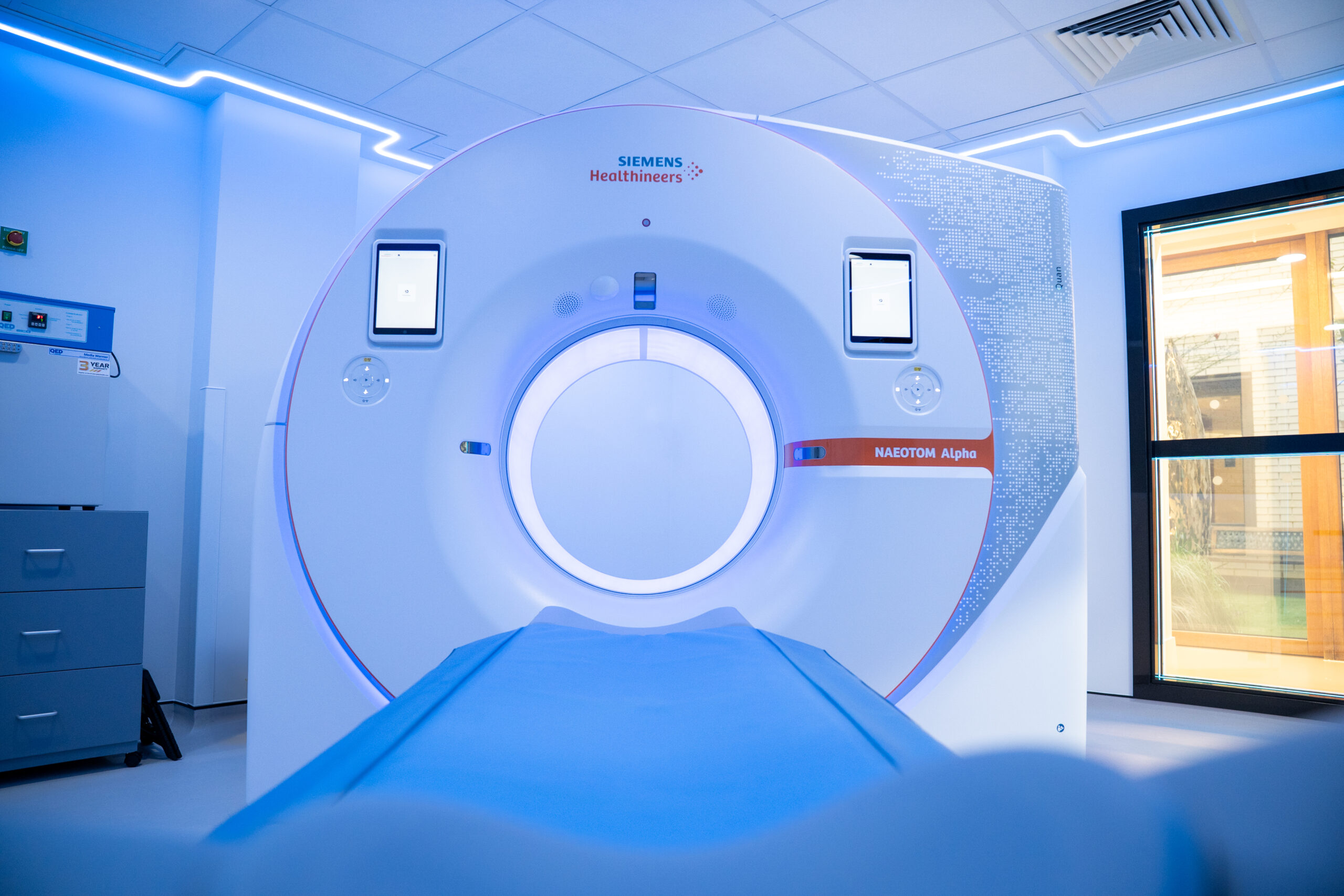
NAEOTOM Alpha CT scanner
The NAEOTOM Alpha is the UK’s first commercially available photon-counting CT scanner. This new technology produces the highest level of image detail when compared to traditional CT scanners.
For example, the scanner’s revolutionary detector enables us to see inside coronary artery stents as small as 2mm in diameter – a feat not previously possible. It also delivers a 45% lower radiation dose than traditional CT scanners.
The NAEOTOM Alpha CT scanner is available at Wimpole Street Consulting Rooms and Diagnostic Centre – the first of its kind in private practice in the UK.
Preparing for a CT scan
Before your appointment, you may be advised – depending on what type of scan you are having – to avoid eating anything for a few hours. This is to help ensure that clear images are taken.
Please inform us if you have any allergies, kidney problems, or if you are taking medication for diabetes, as special arrangements may need to be made.
Please also inform us if you are pregnant. CT scans are not usually recommended for pregnant women unless it is an emergency, as there is a small chance the X-rays could harm unborn babies.
We advise that you wear loose, comfortable clothes and avoid wearing jewellery and clothes containing metal (such as zips),as these will need to be removed before the scan.
What to expect at a CT scan
When you arrive in the CT department, the radiographer (who operates the CT scanner), will explain the procedure to you. They will go through a checklist to ensure that there is no reason that the scan or contrast dye would cause you any undue risk.
The radiographer or doctor will place a cannula in your vein to inject the contrast dye if this is required for the scan. You may also be asked to change into a hospital gown.
You will then be taken to the CT scanner room where you will lie on a bed which moves through a doughnut-shaped scanner. The scanner doesn’t surround your whole body, but it scans small sections of your body as you pass through the ring.
The radiographer will operate the scanner from the next room, but you will be able to hear and speak to them through an intercom. They will ask you to lie still so that the scanner can take clear images without any blurring caused by movement. They may also ask you to breathe in, breathe out and hold your breath at certain points during the scan.
The scan typically takes 10-20 minutes. This time may vary depending on which type of CT scan you are having and which organs or structures in the body require scanning.
Once the scan is complete, the bed will slide back out of the doughnut-shaped ring and you will be free to leave the hospital or clinic, and return to your usual daily activities.
Are there any side effects after a CT scan?
The immediate risk after a CT scan is from the contrast dye used, which can cause minor side effects in some people. Contrast dye is a substance which is used during the scan to show the blood vessels and abnormal tissues in the area being scanned.
Contrast is injected into an intravenous line, but not all CT scans require contrast.
If a contrast is used, the side effects can include:
- vomiting
- hives
- nausea
You may be advised to wait for around 15 minutes in the department following your scan to ensure that you don’t have a reaction to the contrast or begin to feel unwell, but this is rare. Most people experience no side effects at all.
The longer-term risk in people having a CT scan is that of causing cancer over their lifetime as the CT scanners use ionising radiation (just like any X-ray procedure). However, this risk is very small with a lifetime chance of risk being less than 10,000 with one or two scans (our natural risk of having cancer is one in two). It’s important to note that the risk is greater in children and younger people.
Your doctor will weigh the benefit of having the scan compared to any perceived risk before recommending that you undergo a CT scan. If you have any concerns, do not hesitate to speak to team.
Getting your CT scan results
Your scan results will be analysed first by a computer and then by a radiologist, who will write a report and send it to your doctor. We aim to process the results the same day or within a few days, depending on the urgency.
How much does a CT scan cost?
The cost of the CT scan varies depending on which type of scan you have. Our price list is as follows:
- CT coronary angiography: From £1,490
- CT calcification scoring: From £604
- General CT 1-part: From £1,117
- General CT 2-part: From £1,414
Please contact us for a quote.
Locations
We are pleased to offer CT scans to our patients in multiple locations, carried out by our specialist teams.
Discover our team of cardiology specialists
Meet our team of renowned cardiology specialists. From cardiovascular health assessments to innovative interventions, our specialists are committed to delivering personalised care designed just for you.
